What Does an Mri Look Like in a Concussion Due to Shaking
A Visual Guide to Concussions and Encephalon Injuries
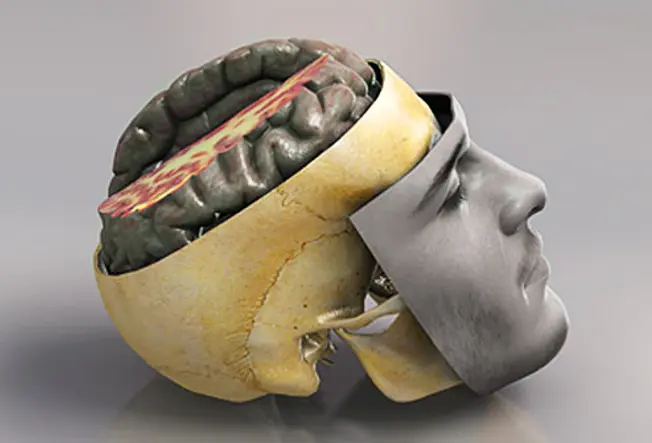
Head Injuries and Your Brain
1 / 22
Your brain is well protected from most damage. Information technology sits inside a hard, bony skull. Layers of membranes and fluid provide extra padding. But even with all this natural protection, injuries still happen. And the damage can affect everything you do, from thinking to moving. A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is any blow to your head that's hard plenty to bear on the brain.
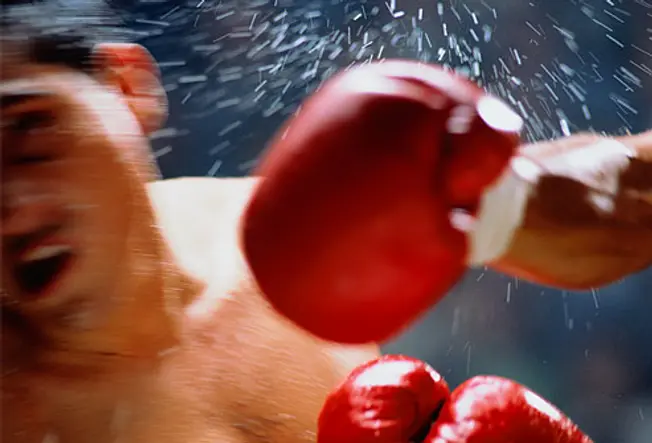

How Does Your Brain Get Hurt?
2 / 22
A hard blow to the head tin milk shake your encephalon inside the skull. The effect: bruises, broken blood vessels, or nerve damage to the brain. A hard striking that doesn't cause bleeding or an opening in your skull could be a airtight brain injury. An open up brain injury is when an object penetrates the skull and goes into your brain.

Brain Injuries: Balmy vs. Severe
three / 22
A TBI can be balmy or severe. A concussion is a balmy TBI -- y'all should recover pretty quickly. A astringent TBI can do enough impairment to knock y'all unconscious for a longer menstruum. It tin can even lead to a coma or death.
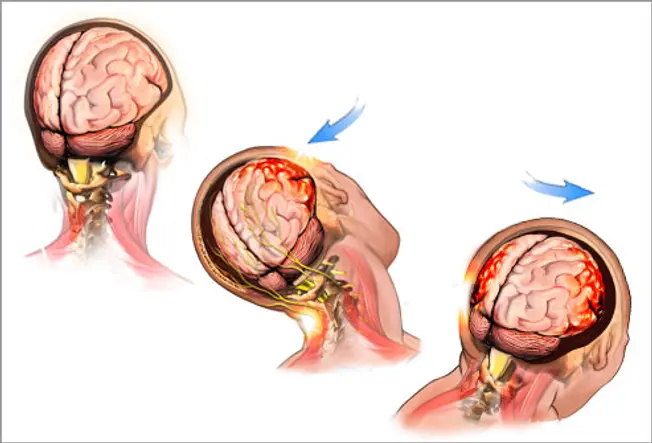
What Is a Concussion?
4 / 22
It's when a jolt to your body or head shakes your brain dorsum and forth within your skull. Any difficult hit -- whether it's from a football tackle or a motorcar blow -- can lead to a concussion. Although information technology'south considered a mild encephalon injury, information technology tin cause lasting damage if yous don't rest long enough afterward to let your encephalon fully heal.
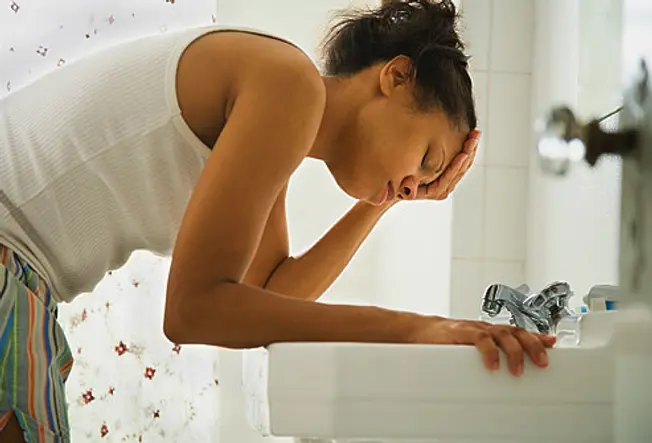

Is It a Concussion?
5 / 22
After a fall or blow to the caput, you may laissez passer out for a few seconds. But many people with concussions don't black out. Telltale symptoms include:
- Dizziness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Blurry vision
- Headache
- Trouble thinking conspicuously
Let a physician check you subsequently a caput injury.
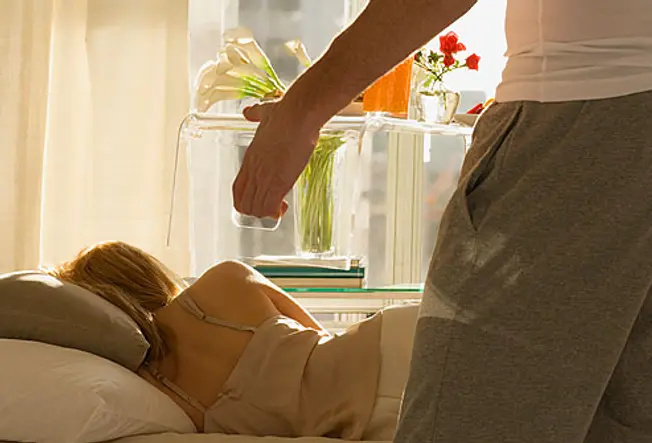

Healing Afterwards a Concussion
6 / 22
Just like you'd rest your ankle later on a sprain, you demand to rest your brain later a concussion. Get plenty of sleep. Ease back into school and work when you start to feel better. Stay off the playing field until your doctor gives you the OK. Getting a second concussion earlier the first ane heals tin can slow your recovery and boost the odds of permanent damage.
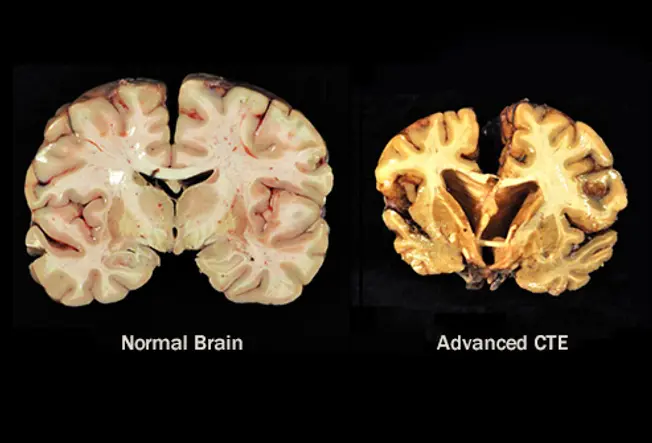
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE)
vii / 22
Football players, boxers, or anyone who gets repeated blows to the head can get this condition, which kills brain cells. A single concussion isn't likely to cause it. Symptoms oft don't testify up for years. At beginning they include problems with mood, behavior, and impulse control. Retentiveness loss, problems making rational decisions, and dementia come subsequently. Doctors tin't diagnose it until after decease, when they can look at your encephalon. At that place's no treatment for the disease, but its symptoms.

Skull Fractures
8 / 22
Your noggin's pretty tough. But if it'southward hit hard plenty, it tin scissure. That'southward called a skull fracture. If the sharp edges of a fractured skull press into your brain, they tin can damage the frail tissues and cause haemorrhage. Watch out for clear fluid from the brain or blood that drains from your olfactory organ or ears.
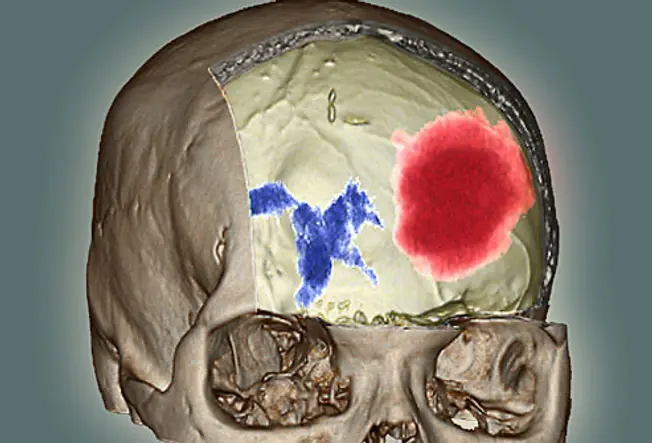
Bleeding in the Brain
9 / 22
Sometimes an injury damages blood vessels inside your brain. The trapped blood pools and forms a bump called a hematoma. Information technology tin can lessen or cutting off claret flow to your brain. This is a medical emergency. Some signs of a hematoma include:
- Headaches
- Vomiting
- Trouble with residue
- Weakness
- Seizures
- Bug speaking
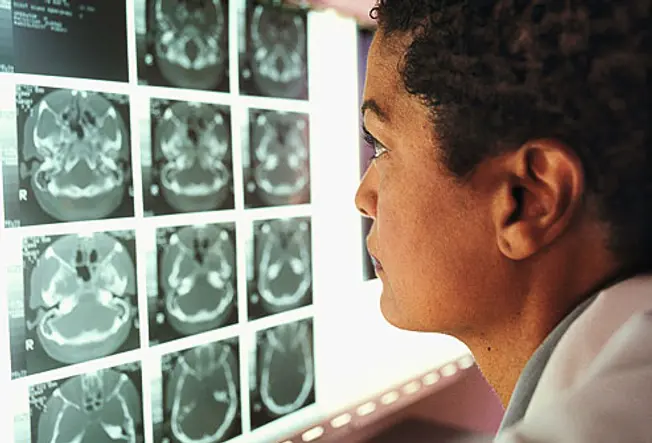
How Are Brain Injuries Diagnosed?
x / 22
Your dr. will do a series of tests. They'll probably ask questions to check your memory, concentration, problem-solving power, and other brain functions. A brain scan called computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can help detect the injury.

Retentiveness Issues
11 / 22
You might damage the parts of your brain that help y'all store and retrieve information. That'll brand information technology harder to remember your birthday, what yous ate for breakfast, or the blow that caused your injury. Some memory problem is normal, but it should come dorsum. Severe encephalon injuries sometimes cause long-term memory loss.

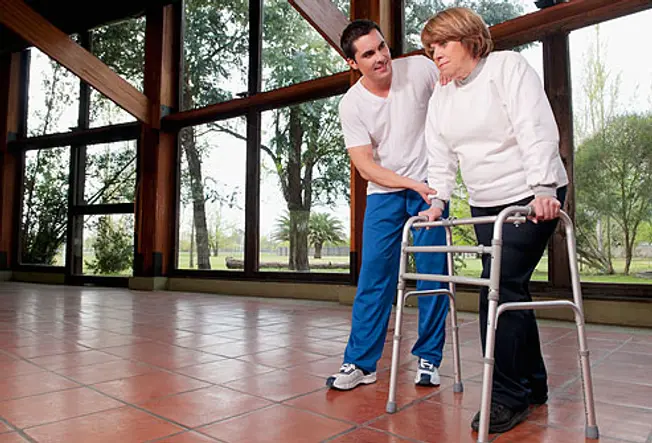
Problems With Movement
12 / 22
An injury tin can touch on parts of your brain that assistance you residual and walk. As a result, you lot may feel dizzy -- like the room is spinning. Or you could damage the part that helps you see clearly and approximate depth. Concrete therapy and other rehabilitation can better your residual and movement subsequently a head injury.
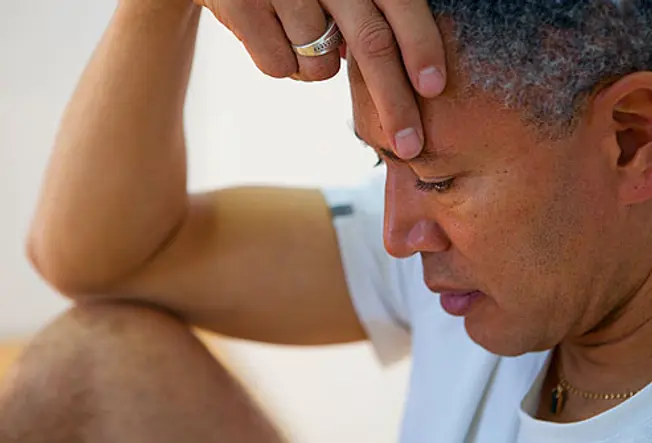

Mood Changes
13 / 22
You may non experience like yourself after a TBI. Up to one-half of people have symptoms of depression, including lingering sadness and sleeplessness. Some have wild mood swings, laughing ane infinitesimal and crying the side by side. Others experience overly aroused or anxious. If you can't control your emotions, talk to your doctor about treatments.

Long-Term Effects
fourteen / 22
A serious encephalon injury tin stick with you for life. Problems thinking, moving, and controlling your emotions may non get away, especially if you've taken many hits to the caput (from sports, for instance). There's some evidence that having a TBI increases your risk for Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's, CTE, and other brain disorders as you get older.

The Recovery Process
15 / 22
For mild injuries like concussions, the best treatment is to residuum and give your brain a risk to heal. Physical, occupational, and voice communication therapy tin help with the physical and mental side furnishings of severe damage. Counseling sessions with a psychologist or psychiatrist can help you learn to live with your injury.

How Common Are Brain Injuries?
16 / 22
Every year, i.seven million people have an accident that leads to a traumatic encephalon injury. Most -- about 75% -- are mild, including concussions. More serious injuries send near 223,000 people to the hospital and crusade nigh 60,000 deaths.

Children and Brain Injuries
17 / 22
They're among the leading causes of disability and death in children. over 800,00 -- more than boys than girls -- visit an emergency room for a brain injury each year in the Us. Kids with TBI tin can have more trouble learning. They may also struggle with behavioral and emotional problems.

Is It Merely a Bump on the Head?
18 / 22
Learning to walk is a wobbly time. An unsteady toddler can take a lot of tumbles. Luckily, kids are pretty sturdy. Well-nigh bounciness right dorsum from a small-scale crash-land on the noggin. But if your child won't stop crying, throws upwards, says their head or neck hurts, or has trouble waking upwards afterward a fall, call the medico right away.
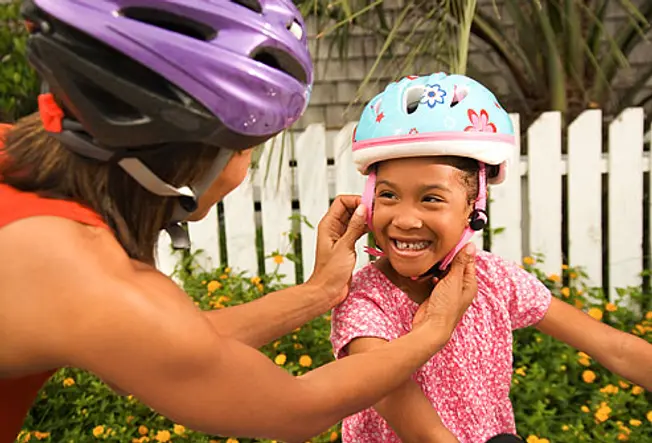

Forestall Kids' Injuries
19 / 22
Toddlers ordinarily get a brain injury later a fall. One time kids reach school age, sports injuries and bicycle and auto accidents are the culprits. Teach kids to wear close-plumbing fixtures helmets and other rubber gear during sports and recreational activities. There is besides a new device called Q-Collar which can be worn to assist reduce movement of the brain. Don't allow them play sports that aren't correct for their historic period. Make sure they follow bike safety rules about traffic and road hazards.
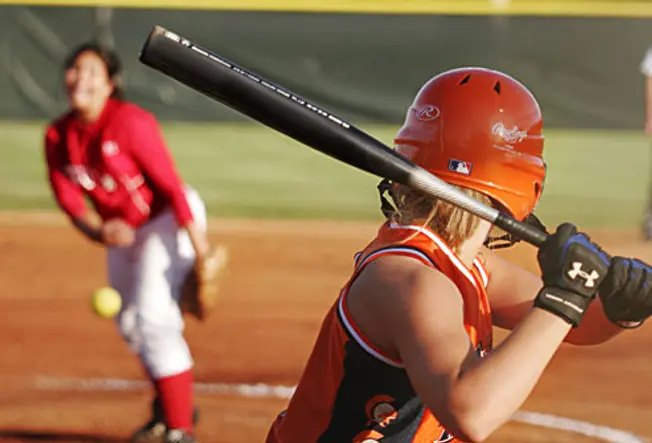

Tips for Athletes
twenty / 22
Blows to the head are common in professional and amateur sports like football, baseball game, and hockey. Some leagues have even inverse policies to prevent injuries and care for them faster and more finer. Vesture a helmet that fits snugly every fourth dimension you play. Obey the rules to prevent falls and head-on collisions.
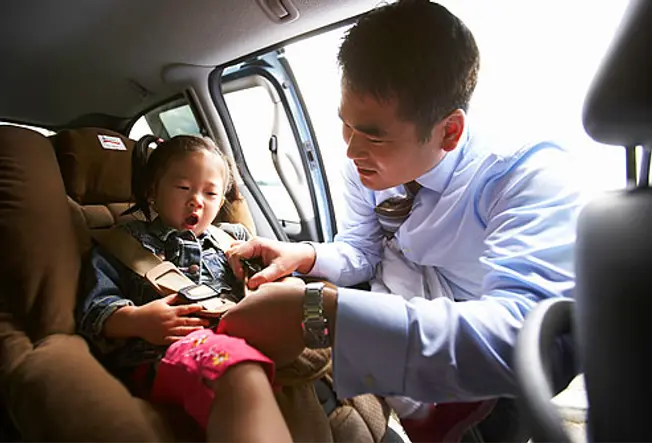

Safe in Cars
21 / 22
An auto accident can thrust your head forward -- or worse, propel yous from the vehicle headfirst. Earlier you put the key in the ignition, put on your seatbelt and buckle your child into an historic period-advisable safety seat. Teach kids to wear seatbelts when they ride on buses or in other people'due south cars. Rear collisions can make your brain slosh around in your skull every bit your head snaps frontward then back.
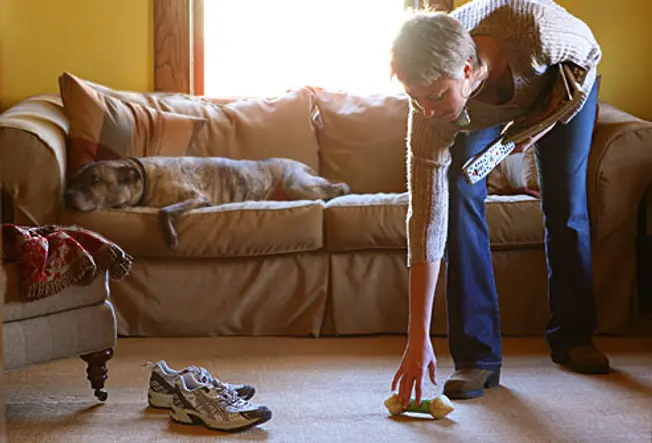

Preventing Injuries from Falls
22 / 22
You don't take to fall far or hard to hurt your head. To avoid taking a tumble, make clean up the ataxia, cords, and other hazards that may cause you to trip. Install lights in halls and stairways then you don't stumble while going to the bathroom at night. Secure all rugs and mats firmly to the floor and then they don't slide effectually under your feet.
IMAGES PROVIDED By: (i) 3D4Medical SOURCES: American University of Family Physicians: "Head Injuries," "Head Injuries--Complications." American Association of Neurological Surgeons: "Sports-Related Head Injury." Brain Injury Association of America: "Diagnosing Encephalon Injury." CDC: "Concussion and Mild TBI," "What to expect after a concussion," "What are the Potential Long-Term Outcomes of TBI?" "Clinical Diagnosis and Management." Concussion Legacy Foundation: "What Is CTE?" Dana Foundation: "Brain Trauma, Concussion and Coma -- The Dana Guide." McGill University: "The Brain from Top to Bottom." Medscape: "Neuropsychiatric Sequelae of Traumatic Brain Injury." "Traumatic Brain Injury in Children." Merck Manual Home Edition: "Skull Fracture." National Broadcasting Center for Children with Disabilities: "Traumatic Brain Injury." National Highway Traffic Condom Assistants: "Kids and Bike Safe." National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke: "Traumatic Brain Injury: Hope Through Research," "NINDS Traumatic Brain Injury Information Page." Nemours Foundation: "Head Injuries," "Concussions." American Psychological Clan. National Football League. National Institutes of Health: "Head Injury." U.S. Department of Health and Human being Services: "Treating Clients with Traumatic Brain Injury." Academy of Washington Medical Center: "Memory and Encephalon Injury." Virginia Republic University: "Emotional Problems After Traumatic Brain Injury." Evidence Sources
(2) Bruce Ayres / Rock
(3) Rubberball
(four) Nucleus Medical Fine art, Inc.
(5) Terry Vine / Blend Images
(6) Image Source
(7) Boston University Center for the Study of Traumatic Encephalopathy
(eight) Zephyr / Photo Researchers, Inc
(nine) Zephyr / Photo Researchers, Inc.
(x) Mike Powell / Digital Vision
(11) Fotosearch
(12) Denkou Images / Cultura
(thirteen) John Lund/Marc Romanelli / Blend Images
(fourteen) Glow Health / Glow
(xv) Don / Pattern Pics
(16) Stockbyte
(17) Leah / Design Pics
(18) Laurence Monneret / Rock
(19) Jupiterimages / Comstock
(20) Jeff Greenberg
(21) Thomas Northcut / Riser
(22) Steve Pomberg / WebMD
Source: https://www.webmd.com/brain/ss/slideshow-concussions-brain-injuries
0 Response to "What Does an Mri Look Like in a Concussion Due to Shaking"
Post a Comment